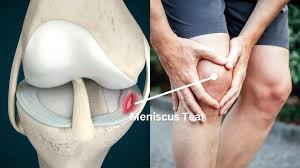
If you’ve been diagnosed with a meniscal tear, you might be feeling confused, frustrated, and worried. Although a meniscal tear is a common knee injury, its seriousness can vary based on how severe it is. With an appropriate treatment plan and physical therapy, you can heal and return to your usual activities. This blog will explain what a meniscal tear is, its causes, symptoms, and how physical therapy can support your recovery.
What Is a Meniscal Tear?
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage in your knee that acts as a cushion between your shinbone (tibia) and your thighbone (femur). Each knee has two menisci: one on the inner (medial) side and one on the outer (lateral) side. These menisci play an important role in absorbing shock, stabilizing the knee joint, and allowing smooth movement.
A meniscal tear occurs when the meniscus is torn, typically as a result of trauma or degeneration. While younger individuals may tear their meniscus due to sports injuries or accidents, older adults can experience degenerative meniscal tears due to years of wear and tear on the cartilage.
Causes of Meniscal Tears
Meniscal tears can happen in various ways. The most common causes include:
1. Sports Injuries
-
Sudden twisting or rotating motions during sports like basketball, football, or soccer can cause a meniscal tear.
-
High-impact activities or awkward landings can also contribute to the injury.
2. Aging
-
As we age, the meniscus naturally becomes more brittle and less flexible, which increases the risk of tearing, even during normal activities.
3. Trauma or Accidents
-
A direct blow to the knee, such as in a car accident or a fall, can also result in a tear.
4. Overuse
-
Repetitive stress from activities like running or heavy lifting can wear down the meniscus over time, eventually leading to a tear.
Symptoms of a Meniscal Tear
Recognizing the signs of a meniscal tear is crucial for proper treatment. Common symptoms include:
-
Knee pain: This pain may be located on the inner or outer side of the knee, depending on the location of the tear.
-
Swelling: A tear can cause inflammation, leading to swelling in the knee.
-
Stiffness: You may find it hard to fully bend or straighten your knee.
-
Popping or clicking sounds: Sometimes, a meniscal tear can cause a sensation of popping or clicking when moving the knee.
-
Instability: Some patients feel like their knee is “giving way” or feels unstable when walking or standing.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
How Physical Therapy Helps in Meniscal Tear Recovery
Physical therapy is a critical component of recovery for meniscal tears. While surgery may be necessary for some severe tears, many people can recover with conservative treatments, including physical therapy. Here’s how physical therapy plays a role:
1. Pain Management and Inflammation Reduction
-
Ice and Heat Therapy: Physical therapists can use modalities like ice and heat to reduce swelling and manage pain.
-
Electrical Stimulation: This can help reduce pain and promote healing by stimulating the muscles and tissues around the knee.
2. Strengthening the Muscles Around the Knee
-
Strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles helps provide stability and support to the knee joint.
-
A strong muscle group around the knee reduces the strain on the meniscus, preventing further damage and promoting faster healing.
3. Improving Range of Motion
-
A torn meniscus can make it hard to fully bend or extend the knee. Physical therapy exercises focus on gently stretching the knee joint to improve flexibility and prevent stiffness.
4. Proprioception and Balance Training
-
Re-establishing proper balance and proprioception (your body’s awareness of its position in space) is key for preventing falls and regaining normal movement. A physical therapist will work with you on exercises that enhance your balance and coordination, which are often affected by knee injuries.
5. Education and Activity Modification
-
Your therapist will educate you on how to modify your movements and activities to avoid further damage to the knee while you recover.
-
Proper body mechanics, posture, and technique during everyday tasks are essential for a full recovery and to prevent future injuries.
6. Gradual Return to Activity
-
A well-structured rehabilitation plan will help you return to normal activities in a safe and controlled manner. This includes sports, running, or simply getting back to your daily routines without risk of re-injury.
Surgery: When Is It Necessary?
While most meniscal tears can be treated non-surgically with physical therapy, there are cases where surgery may be necessary. This typically involves meniscal repair or partial removal (meniscectomy) of the damaged tissue.
Surgery might be required if:
-
The tear is large or located in an area with poor blood supply, where healing is unlikely without surgical intervention.
-
Conservative treatments fail to provide relief, or the knee remains unstable.
After surgery, physical therapy will still play a crucial role in your recovery by promoting healing, restoring strength, and improving mobility.
Conclusion
A meniscal tear may seem daunting, but with the right treatment and commitment to physical therapy, you can return to full function. The goal of physical therapy is to reduce pain, strengthen the muscles around the knee, and restore movement. Whether you’re recovering from surgery or opting for a non-surgical approach, working closely with your physical therapist is essential to ensure the best possible recovery.
If you suspect a meniscal tear, don’t wait. Early intervention and proper rehabilitation will improve your outcomes and speed up your recovery. So stay positive and stay active—your physical therapist will guide you every step of the way!