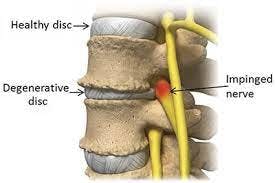
Intervertebral Discs
The intervertebral discs are localized in between all the vertebrae except for the atlanto–axial and sacral vertebrae.
The intervertebral discs function to allow movement of the spine, absorb shock and transmit loads through the vertebral column.
The intervertebral discs undergo wear and tear over time, no matter what we do.
What is Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)?
Degenerative disc disease isn’t actually a disease but refers to a condition in which a damaged disc causes pain and/or numbness and tingling.

Over time, almost everyone’s discs break down, but not everyone experiences pain.
The incidence of pain and dysfunction related to disc degeneration gets higher with greater levels of wear on the discs. While DDD symptoms can be seen at any age, the prevalence is higher in older patients. According to studies, about 40% of individuals over 30 have disc degeneration that’s visible with medical imaging. These population may or may not have associated symptoms. In populations over 50 and up, 90% of patients have evidence of disc damage.
What Are the Earliest Indicators of Degenerative Disc Disease?
In early stages of DDD, pain often present in the form of radiating, sharp or stabbing sensations with a sensation heat or burning. This pain usually subsides with changes in position. Aside from pain, DDD can also bring about muscle tension or spasms, numbness or tingling in the arms and legs from a compressed nerve.
A physical examination and diagnostic imaging of the intervertebral discs, like X-rays, MRIs or CT scans are necessary to formally diagnose DDD. However, there are a number of characteristic symptoms of DDD you can look out for.
If you suspect you are at risk for DDD, beginning physical therapy treatment sooner rather than later can quickly reduce or eliminate back pain and improve your outcomes.
If you have signs and symptoms, contact our office today to see one of our specialists.


